Plastics are essential to car chassis design, providing lighter weight, higher stiffness, and lower cost than traditional materials. Innovations in plastic technology display successful structural applications each year. It would not be possible to achieve many of these enhancements as efficiently and with the same performance using other materials. Plastics are strong and lightweight — bolstering the chassis/structure of the vehicle.
Car Chassis Design

Plastic and polymer composite lightweighting can increase fuel efficiency substantially. A reduction of just 100 pounds can mean an increase of 6-7% in vehicle fuel efficiency. That’s 6-7% every day for the entire life of a vehicle! The vehicle chassis could represent the single greatest opportunity to reduce weight.

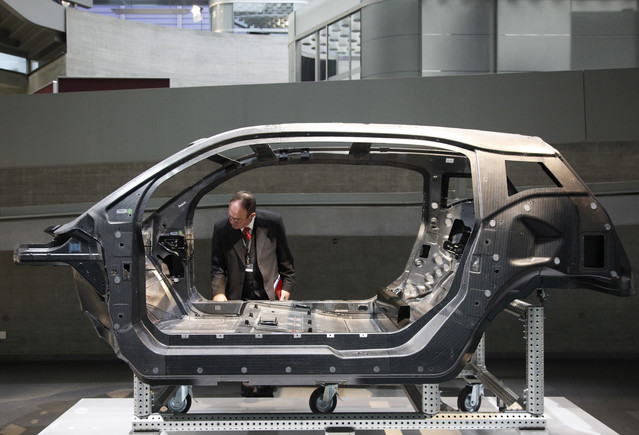
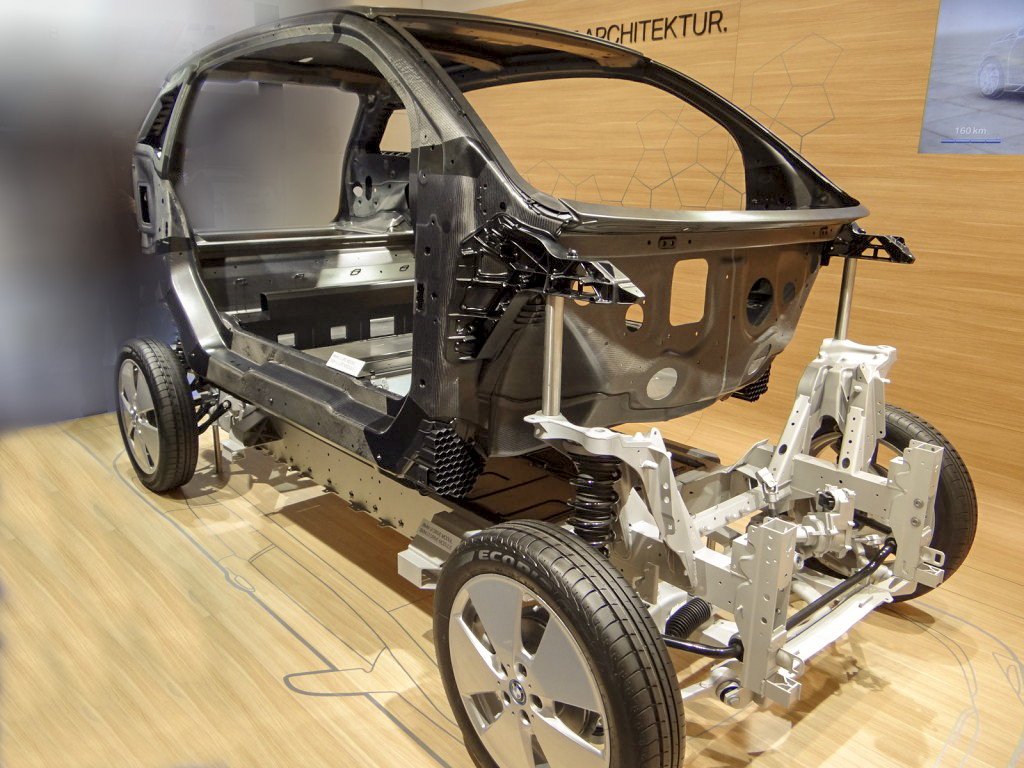
BMW pioneered the i3 which uses a carbon fiber-reinforced plastic for its chassis. The chassis is the structural backbone of a vehicle. For safety and longer range, BMW chose a plastic composite chassis structure.
In this exclusive video, Franz Storkenmaier, of BMW highlights automotive lightweighting. See the dynamic front-end crash vectoring technology at work in the electric BMW i3.
The 2016 Mercedes-AMG C-Class features a pultruded high-performance carbon composite strut. It improves NVH, corrosion resistance, and the stiffness to weight ratio. All this while reducing mass by 45%. The 50K tow unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced epoxy also features a fiberglass layer. This insulating fiberglass layer to resist stone chipping and corrosion.
The nylon glass composite used as a cross-member to support the rear differential. According to SPE, the first such application debuted in the 2016 Mercedes S-Class. Replacing traditional metals reduced transmission noise and mass by 25%.
Plastics and Sustainability: A Valuation of Environmental Benefits, Costs and Opportunities for Continuous ImprovementCar Chassis Structure & Hardware

Advanced plastics, polymer composites, and carbon fiber-reinforced plastics enable remarkable improvements in car frames. These improvements can be seen in safety, design, and performance. Enter a whole new era in vehicle sustainability. Plastics enable vehicle structure and hardware in many different ways.

New material formulas and technology are making vehicles lighter and increasing fuel efficiency. Increased battery range and more flexible, aesthetically pleasing design are additional benefits.

The 2014 Dodge SRT Viper features a drop-in autoclave-cured carbon fiber-reinforced composite engine X-brace. It is 50% lighter than its previous aluminum counterpart but meets stiffness requirements. An exposed-weave finish compliments the same finish found on the underside of the hood.
The 2014 Ford Edge Sport featured an integrated rear camera retention/attachment device. This innovative device is injection molded from PA 6/6, replacing 4 separate parts and reducing costs and labor. It positions the camera to minimize rotation and movement. This can help prevent distorted views.

A blow molded grille reinforcement adds stiffness to the chromed ABS grille assembly on the 2016 Nissan Titan. Cost and weight were each reportedly reduced by 25% vs. a stamped steel reinforcement solution. During production, excess material is punched out and then reprocessed to form subsequent parts.
The 2016 Ford Shelby GT350 Mustang sports a carbon fiber composite grille-opening reinforcement 2-piece injection molded box-section design. The new design reportedly reduced component mass by 24% and NVH values by 2Hz.
Stay Up to Date
Sign up to receive our newsletter and get the latest delivered to your inbox.
The Insider's View
Follow our blog for a unique look at how plastics are changing the way we make cars.
Read